Imagine a world where customer queries are answered instantaneously, supply chains are optimized to perfection, and healthcare diagnostics are revolutionized — all without human intervention.
Sounds like science fiction, right? It’s not. It’s the reality that intelligent automation (IA) is beginning to deliver across various industries.
IA transforms how businesses operate and compete. Whether you want to improve customer engagement, streamline your operations, or stay ahead of the curve — this article’s for you.
What Is Intelligent Automation?
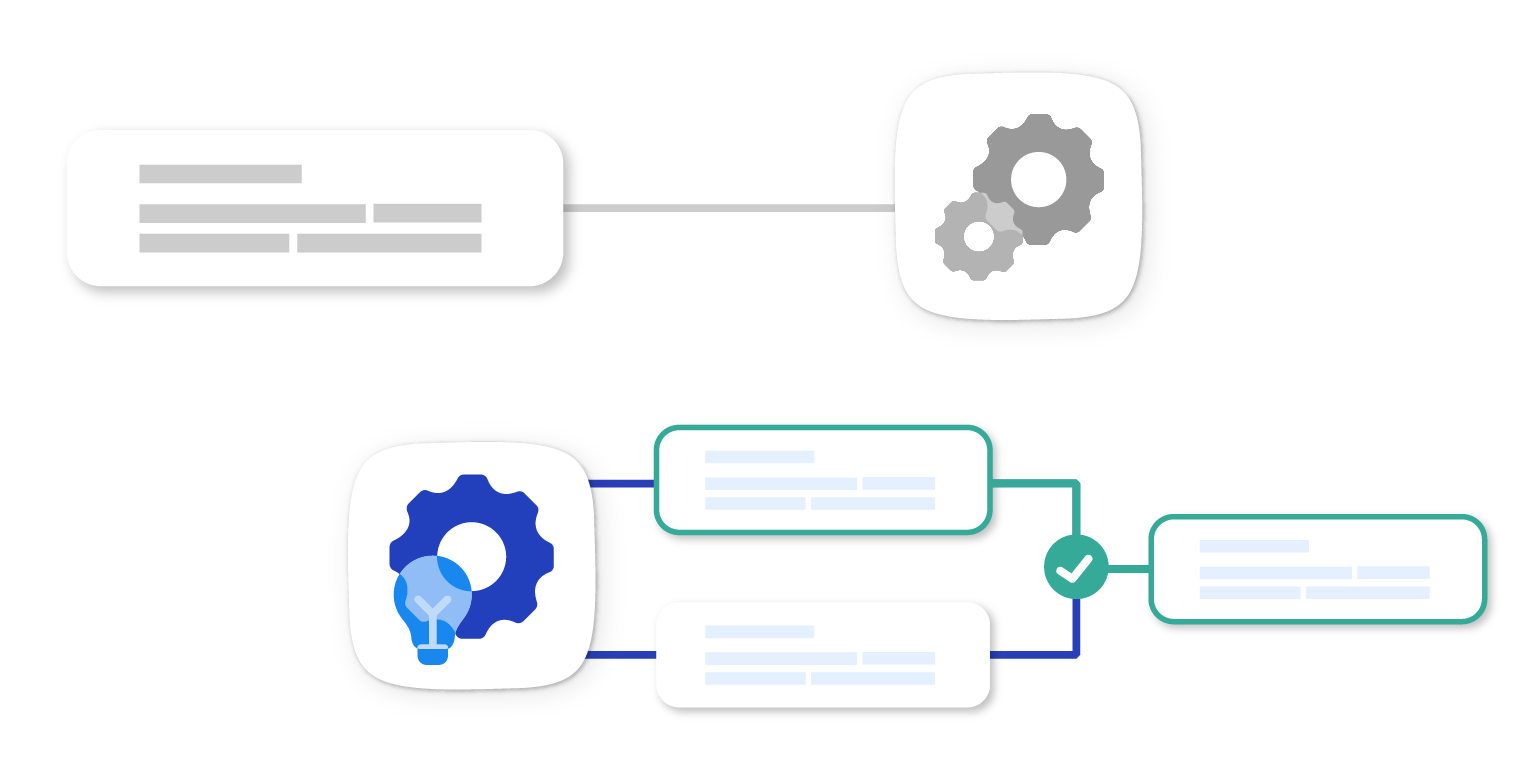
Intelligent automation (IA) is the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies with automation.
It refers to the application of AI and related technologies, including machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and cognitive automation to create and manage automated processes that can adapt and improve over time.
Traditional automation relies on predefined rules and instructions to carry out repetitive tasks. IA, on the other hand, adds a layer of intelligence, allowing automation to handle more complex tasks, make decisions, and even learn from its experiences.
Ultimately, over time, intelligent automation learns how to mirror your most valuable team members’ judgments and actions.
An Example of Intelligent Automation?
Let’s look at this through the lens of IA in banking customer service. Here’s the scenario:
A bank wants to enhance its customer service by offering around-the-clock personalized support. It implements an intelligent automation system integrating robotic process automation (RPA), natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and AI-powered analytics.
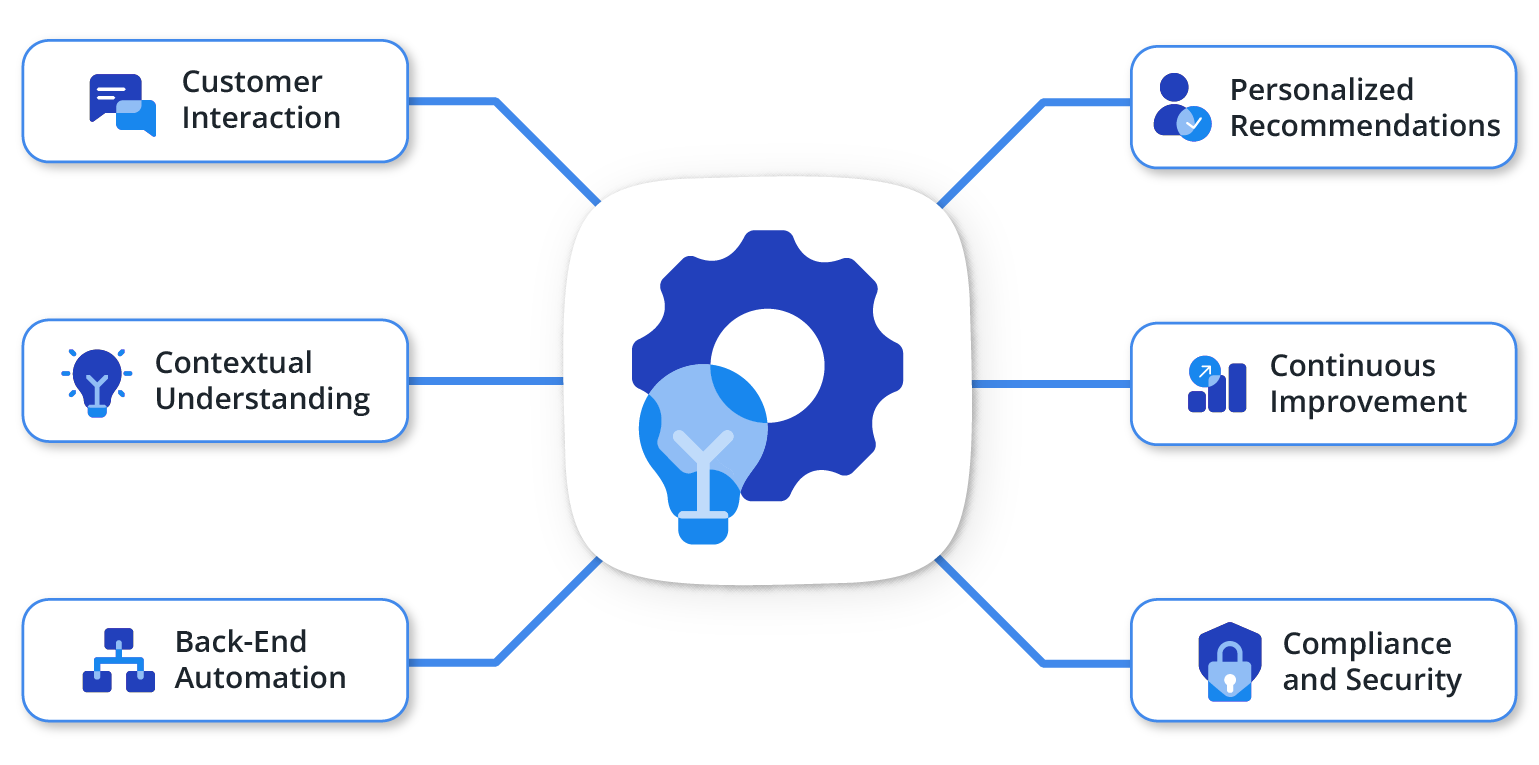
How it works:
- Customer Interaction: Customers chat with an AI-powered chatbot about their account details, loans, or credit cards. The chatbot, powered by natural language processing, understands the customer’s queries and responds in real-time.
- Contextual Understanding: The chatbot applies the context of the customer’s needs, asks relevant questions, and can escalate to a human agent if necessary.
- Back-End Automation: With robotic process automation, the system instantly accesses and updates the bank’s databases, processing transactions seamlessly.
- Personalized Recommendations: Machine learning is applied to analyze customer behavior and offers tailored banking products or investment advice.
- Continuous Improvement: The system learns from interactions, enhancing its abilities over time.
- Compliance and Security: From beginning to end, the intelligent automation workflow ensures adherence to regulations and secures sensitive information.
By leveraging these features, the bank elevates its customer experience by making it more responsive, personalized, and efficient.
The Pros & Cons of Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation offers a number of compelling advantages but introduces some challenges as well. Here’s a look at both:
Benefit: Increased Efficiency
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, IA allows businesses to complete work more quickly, freeing up employees for more complex tasks.
Benefit: Cost Savings & Enhanced Accuracy
While there may be initial costs to implement IA, it can lead to significant savings by reducing labor costs and financial liability caused by human error over time.
Benefit: Scalability
IA systems can handle large volumes of work without significant increases in cost, making it easier for organizations to scale operations.
Benefit: 24/7 Operation
Automation doesn’t require breaks or sleep, so systems can operate around the clock, offering constant service and/or production.
Benefit: Personalized Services
Through machine learning and data analysis, IA can provide more personalized services or products, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Benefit: Predictive Insights
IA can process and analyze vast amounts of data and provide predictive insights to drive strategic decision-making.
Benefit: Empowering Human Workers
By automating mundane tasks, human workers can focus on more creative, strategic, and fulfilling activities.
Drawback: High Initial Investment
Implementing IA can be exorbitantly expensive and is currently only accessible to large organizations. The cost involves purchasing advanced technology, integrating it into existing systems, and training staff — adding up to a substantial investment.
Drawback: Dependent on Data Quality
Machine learning models and decision-making processes are made or broken by the organization’s data quality. Inaccurate, poorly structured, or biased input can lead to undesirable outcomes.
Drawback: Job Displacement
Automation can lead to the loss of jobs, particularly in roles that are strictly composed of repetitive tasks. This can cause a ripple effect on your team’s mental well-being and morale.
Drawback: Complex Implementation
Integrating IA into existing systems and processes can be difficult, often requiring expertise in multiple domains.
Drawback: Security and Compliance Risks
With increased automation comes the need to ensure that processes are secure and compliant.
Drawback: Lack of Emotional Intelligence
IA lacks human emotional intelligence, which may cause negative outcomes for any process that relies on empathy, judgment, or a nuanced understanding of human emotions.
Drawback: Maintenance and Monitoring
IA requires ongoing upkeep for optimal performance and ROI. Unexpected errors or failures can lead to disruptions.
Drawback: Potential Bias
If not carefully designed and monitored, IA systems can inadvertently introduce or perpetuate bias, leading to unfair or unethical outcomes.
IA vs. RPA: Which Is Right for You?
Intelligent automation (IA) and robotic process automation (RPA) are both transformative. While both aim to optimize processes and enhance productivity, their capabilities vary from one another significantly.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for organizations exploring automation. Let’s explore what sets these two technologies apart.
Scope of Automation
IA is capable of complex decision-making, learning, and adaptation via AI, machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. It’s designed to handle multifaceted tasks that require intelligent reasoning and continuous improvement. It’s the closest that automation technology has come to human cognition.
On the other hand, RPA primarily focuses on automating rule-based, repetitive tasks that follow a clear set of instructions. Unlike IA, RPA doesn’t involve decision-making or learning, and is generally employed for straightforward, repetitive tasks.
Complexity
IA can be used to automate complex tasks, can adapt to changes, make decisions, and even learn from experience. It can handle sophisticated challenges that require nuanced understanding and continuous refinement.
RPA, on the other hand, automates more predictable tasks and operates by following predefined rules. Unlike IA, RPA can’t adapt or make decisions, and is typically used to execute routine, repetitive tasks without deviation or improvement over time.
Integration with Other Technologies
IA often requires multiple technologies and enables a broader range of applications.
RPA also often integrates with other systems, but its integration is generally to perform rule-based tasks. Unlike IA, it’s exclusive to automating predictable, repetitive processes.
Cost and Implementation
IA generally requires a larger investment in technology and expertise due to its complexity, data structure, advanced integrations, and customized solutions.
RPA is typically easier and less expensive to implement. Its focus on automating specific rule-based processes means it can often be deployed more quickly and at a lower cost.
While IA offers broader capabilities and can handle more complex tasks, RPA provides a more targeted and economical approach to automating routine operations.
Applications
IA is suitable for complex tasks in customer service, healthcare, advanced financial analysis, and more.
RPA is best suited for data entry, file management, and simple process automation.
Common Use Cases for Intelligent Automation
Here are some key areas where IA is making a significant impact:
Customer Service
As discussed earlier, IA in customer service handles real-time queries, offers personalized recommendations, and escalates issues when needed.
By providing 24/7 support and analyzing customer behavior, IA improves customer experiences and significantly reduces operational costs.
Supply Chain
IA-powered supply chain management forecasts demand, optimizes inventory, and improves supplier collaboration.
By identifying inefficiencies and adjusting in real-time, IA enhances efficiency, minimizes waste, and supports agile decision-making.
Healthcare Diagnostics and Treatment
In the healthcare sector, IA transforms diagnostics and treatment planning by analyzing large data sets. It can detect diseases like cancer earlier through image analysis and assist in crafting personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s genetic makeup and history.
By increasing the accuracy and personalization of care, IA helps healthcare professionals make better-informed, patient-centered decisions.
Embracing the Power of Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation represents a massive leap in technology.
From providing seamless customer support to optimizing supply chain management and revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics, it delivers efficiency, accuracy, and intelligence to age-old processes.
However, leveraging the full potential of IA requires significant investment, a deep understanding of its capabilities and limitations, careful planning, and strategic implementation.
IA can be the key to enhancing customer engagement, streamlining operational processes, or unlocking new insights in data-driven fields. With its diverse applications, it’s more than a tool. It’s a strategic asset that can propel your organization to new heights.
Ready to achieve unprecedented operational efficiency powered by intelligent automation? Partner with Kizen for tailored IA solutions that align with your team’s unique challenges and goals. Contact us today and take the first step toward a smarter, more efficient future.